What is a Search Engine?
A search engine is a software system that enables users to search for websites and information on the internet. These engines work by crawling millions of web pages and indexing them according to several scoring methods performed by the algorithm. When you make a search, the search engine uses this indexed data to provide users with a list of web pages that are most likely to contain what they’re looking for in order of relevancy.
These systems have shaped the way we use the internet to look for information and have spawned the birth of an entire industry of SEO professionals helping businesses try and crack the algorithm’s code and rank higher.

How Do Search Engines Work?
Search engines use complex algorithms to scan “crawl” and index web pages across the internet so that they can be used by users that are searching for information on various topics. They’re essentially creating a phonebook for all of the websites on the internet; except that ranking first in this phonebook is much harder than in the alphabetical order of a phonebook. You can’t just name your business AAA Law Firm anymore. These algorithms are constantly being updated and improved, in order to make sure searches are accurate and up-to-date.
The search engine process can be simplified into 3 main core steps. crawling, rendering, indexing, and ranking. Take a look at the image below to get an idea of how Googlebot crawls web pages:
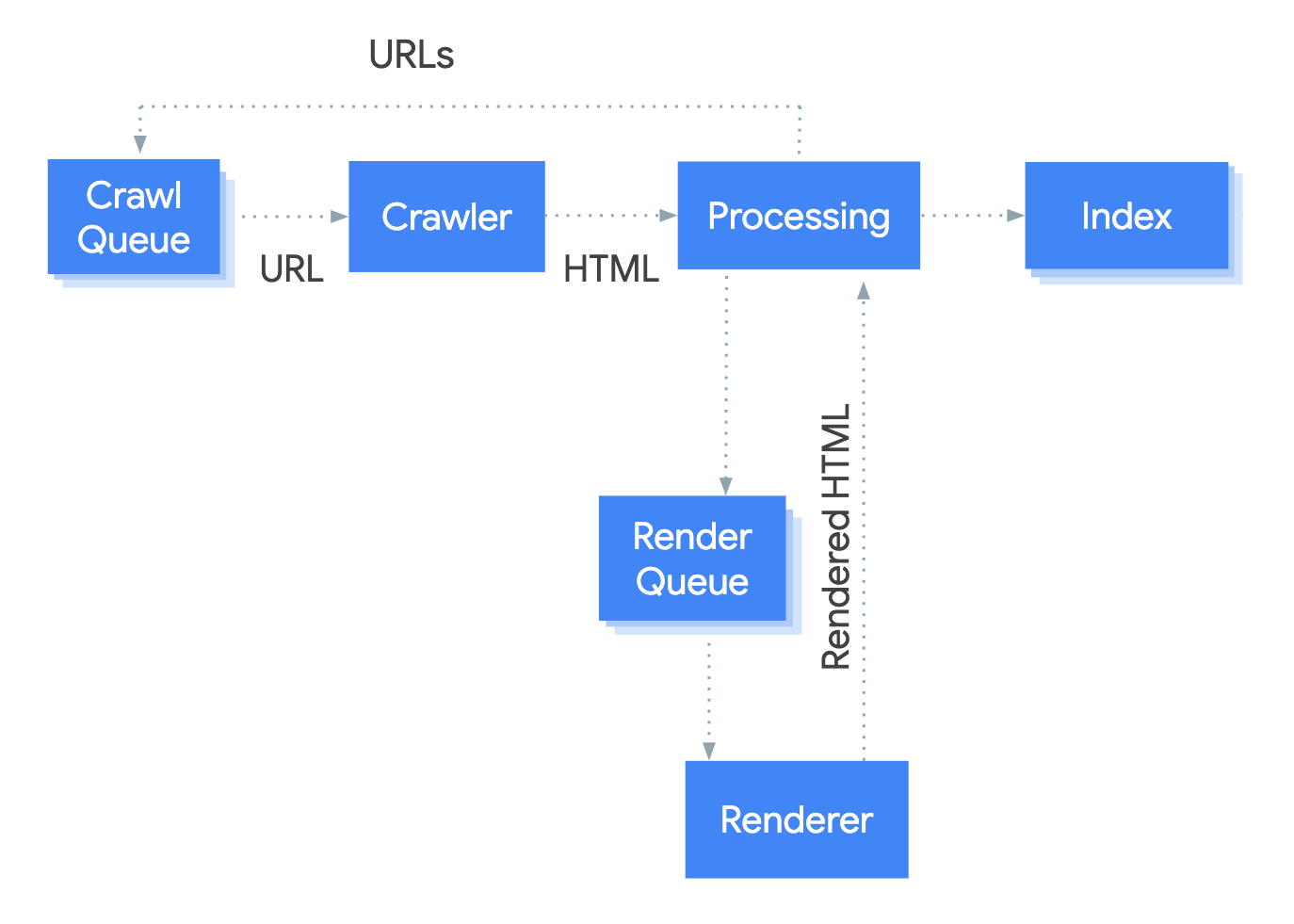
Crawling
First, the search engine crawls websites, which means it visits each webpage and follows links on them. It collects data on everything it finds (content, images, videos). Then this crawled data is indexed. When Google discovers a URL, it will crawl the page to determine what it’s all about. During this crawl, the page’s javascript and content are rendered.
Websites are able to tell Google that they don’t want their page indexed by placing a noindex HTML tag on the website. It looks like this:
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex“/>

Indexing
Once the page is crawled, Google indexes it and tries to figure out what the page is about. The process of indexing involves processing and analyzing the textual content and key content tags and attributes, such as <title> elements and alt attributes, images, videos, and more.
Google claims that during the indexing stage, they look for duplicate content and correct canonical tags. They then analyze the content of each webpage and decide how relevant it is to certain keywords or phrases that users type into their search query. Search engines use many signals and advanced algorithms to determine which web pages should appear at the top of a list of results when someone makes a query.
Some examples of search engine ranking signals:
- The number of incoming links to a page (Backlinks)
- Content Quality
- Page load speed
- The navigational structure of the website (Technical SEO)
- The presence of keywords in the page title and other meta tags
- The freshness of content on the page
- User experience
The data collected by the crawler is indexed (hence the name of the process) in a database. This essentially means that it’s labeled and organized into categories, so when a search query is made, the search engine can quickly find the most relevant results. The index is constantly being updated as new content is published or removed from websites.

Ranking
Once the data has been indexed and organized, the search engine algorithm will rank each webpage according to its relevance to user queries. It looks at several factors such as how often certain keywords are used on a page; whether those words appear in titles, headings, or other elements on the page; how many other websites link to it; how long people stay on it; and more.

The Technologies Used in Search Engines
To ensure precise, current results, search engines employ innovative advancements like machine learning algorithms to identify trends in data; NLP models to interpret language meanings; and AI-driven deep neural networks that can analyze images and videos. All of these cutting-edge solutions are used together toward the common goal of optimizing accuracy for search engine outcomes and increasing relevant quality search results for their users. Google’s #1 goal is to show the most relevant content for that particular search query.
Search engines harness the power of several innovative technologies including natural language processing, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and data mining/analysis to determine which webpages match up each inquiry. They also track trends in user behavior in order to improve their algorithms over time so they can offer more accurate results. Search engines may also consider other factors such as page speed, mobile compatibility, and even user reviews when ranking websites.
Best Practices
For webmasters seeking higher visibility on Google, Search Central offers key best practices that prioritize content and connections. The goal is to create high-quality helpful content that is people-first. With these guidelines in place, increasing your website’s reach via Google has never been easier!
⚙️ SEO Best Practices:
- Create quality content that informs and helps people
- Answer commonly asked questions (People Also Ask – PAA)
- Perfect the technical component of your website and ensure Google can crawl it
- Be active and promote your services or web pages in online forums
- Follow best practices for Javascript SEO
- Enable schema data and markup for rich content snippets and appear more prominent in search engine results pages
Furthermore, having high-quality links to your web page from websites with a good reputation will make Google take notice. These links help inform Google that other trusted websites believe that the content on your webpage is best suited for a given subject. For instance, if you sold pet supplies and got a link from an established pet blog, this would be a great signal to Google that your website is a reputable source of information about pet supplies, resulting in a better position in search results.

How do I check if my website is on Google?
If you want to see if your website is being indexed by Google go to google.com and type in site: followed by your website address site:example.com. For example, for our website, we would type in site:voxdigital.ca
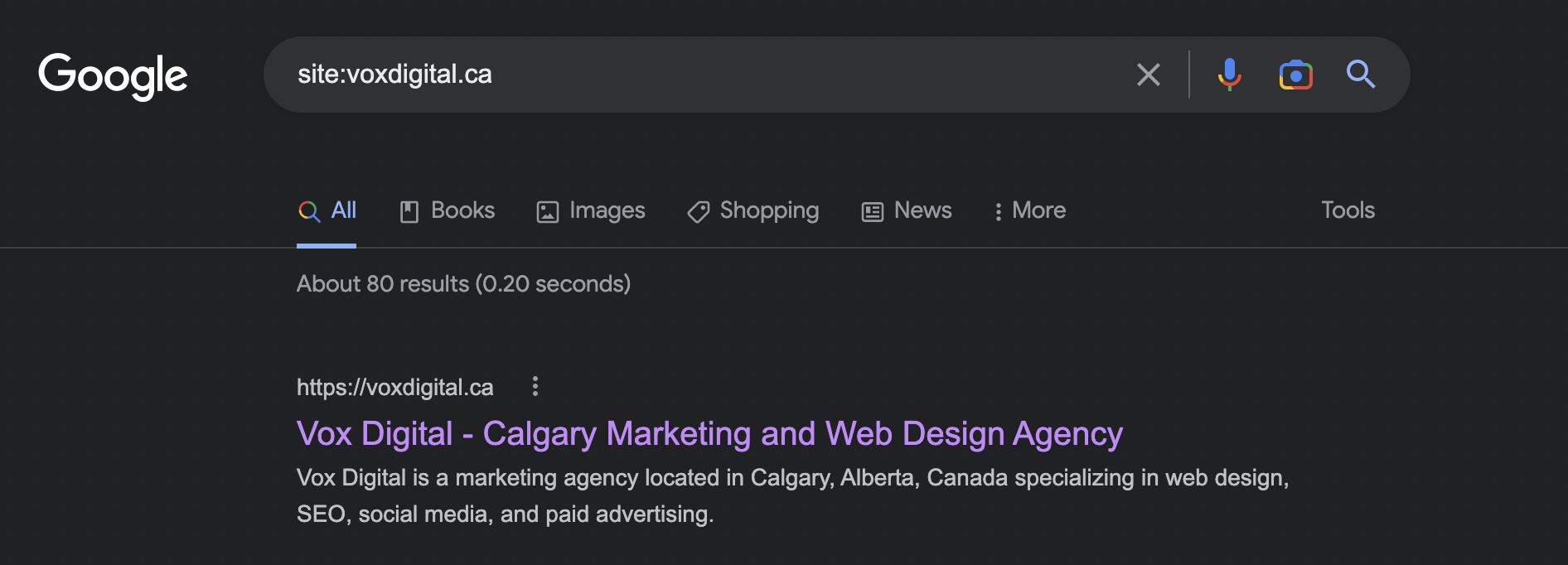
The results will show you if Google has indexed your website, and it will also show you how many pages it has indexed. If you don’t see any results here, read into the next section to determine how to fix your problem.
How do I get my website in Google search results?
In order for Google to take notice of your website and rank it highly for relevant searches, you need to make sure Google can even find your website in the first place. 🔑 Here are some key aspects you need to make sure you’re covering when you want Google to crawl and index your pages.
- Use a descriptive <title> tag on each page.
- Use descriptive meta descriptions on your web pages.
- Make sure you aren’t blocking Google in your robots.txts file (usually located at robots.txt)
- Create a website sitemap.xml and submit it to Google Search Console
- Test your website using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test
Google also provides a basic checklist for appearing in Google Search results.
Title Tags
A title tag is an HTML tag that describes the content of the webpage. It’s the text that you see in your browser tab when you visit a website.
For example, on this current post, if you’re viewing it on Google Chrome on a desktop, it probably looks something like this:
 We include the post title within the title tag so users and search engines know what this page and topic are about. Google has never officially confirmed a suggested title tag length but we suggest sticking to around 60 characters.
We include the post title within the title tag so users and search engines know what this page and topic are about. Google has never officially confirmed a suggested title tag length but we suggest sticking to around 60 characters.
You can also test your title tags using Mangools SERP Simulator
Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions are similar to title tags, just that they contain a more informative description of the website. Again, just like with meta titles Google has no suggested character length but we suggest keeping it around 160.
Create a Sitemap
A sitemap is a file that contains a list of pages, images, videos, and various other file types found on a website. This file is usually located at example.com/sitemap.xml. It helps search engines like Google crawl your website more efficiently as you’ve provided them with a list of all crawlable content. Massive websites with hundreds of thousands and millions of pages need to conserve their crawl budget, and creating these sitemaps help do just that.
Here’s an example of what a sitemap looks like:
When users enter their query into a search engine, it searches its vast index of websites using keywords and other data points related to the search term. Then it ranks the results according to relevance and provides users with a list of web pages that most closely match their query. This process happens almost instantaneously and helps users get the information they need quickly and easily.
Overall, search engines are an essential part of today’s online world because they make it easier for us to find relevant information on virtually any topic or keyword we can think of. By leveraging powerful algorithms and technologies like natural language processing and machine learning, search engines help us access the information we need quickly and efficiently without having to sift through multiple sources manually.
How do search engines rank websites?
To accurately rank webpages, search engines use several factors such as the relevancy of the content, how many other websites link to it, and how often keywords appear on the page. This helps determine which pages should come up first in the search results. Search engines also take into account user behavior such as past searches and click-through patterns when ranking pages.
Some key ranking factors for the Google search algorithm include:
- High-quality content
- Backlinks
- Keyword usage in the title, meta tags, and website content
- User experience (UX/UI), including site speed and mobile-friendliness
- Mobile-friendliness
- HTTPS SSL certificate
- The freshness of the content (Maybe it’s time to update that old dusty blog post from 2019?)
- Structured data and schema markup
It’s important to note: Google has not publicly released a comprehensive list of ranking factors, and the importance of each factor may vary depending on the search query and the industry.
Chase Keating
Chase Keating specializes in website design and digital marketing. He is the founder and creative director at Vox Digital. Click here to book a time to talk with us!
Informative post Chase! I took a look and noticed my sitemap included some URLs I didn’t want Google indexing. Thanks for the pointer.
Thanks Greg. Glad I could help. I suggest regularly checking your sitemap to make sure nothing’s in there that shouldn’t be!
Interesting. I never knew about the implications of having a ton of Javascript on my website. I’m definitely going to see how it’s getting rendered by Google in search console. I appreciate the help Chase. Another solid chunk of information yet again. Keep it up bro.
Thanks for the feedback Luke! Yes, always double-check search console to see how Googlebot is rendering your pages – I’ve found tons of issues this way.
Whoa. There’s so much great information about search engines here I’m going to have to come back a few times to digest everything.
Thanks for your kind comment Anna!